Maltodextrin is known as a sugar and starch substitute in foods. The carbohydrate is used as a component in children's and sports nutrition, in dietetics and cosmetology. Nutritionists pay attention to the fact that a substance can, both be beneficial to the body, and some harm in certain cases of use.
Maltodextrin - what is it?
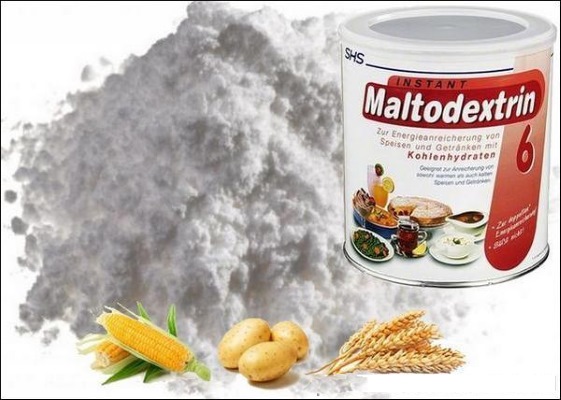
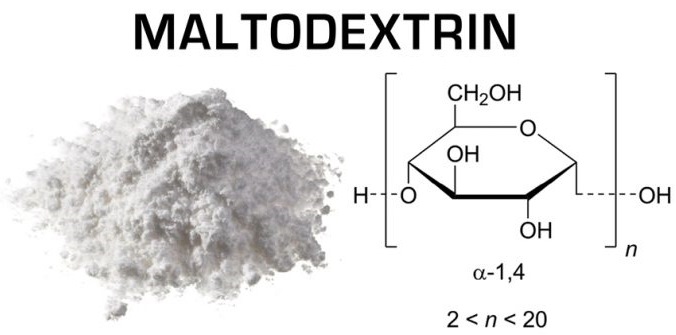
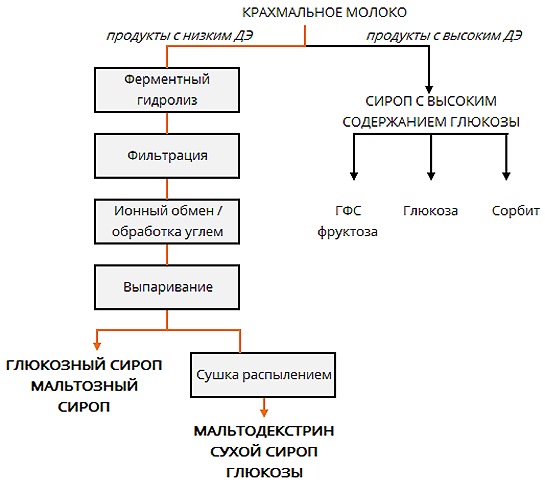
Maltodextrin - Multi-Component Fast Carbohydrate Blendalso known as "molasses" and "dextrinmaltose", composed of glucose, maltose, maltotriose and dextrin molecules. With the complete breakdown of the substance, glucose is formed. It is obtained by enzymatic breakdown of vegetable starch.
In most cases, this is done using cornstarch, often made from genetically modified corn. Rice, wheat and potato starches are also used as raw materials. Enzymes break the elongated starch chain, consisting of glucose, into fragments (dextrins) containing from 2 to 20 glucose molecules.
Maltodextrin has a fairly high glycemic index (105-136), which is due to the gastrokinetic properties of the substance, the polysaccharides of which can quickly enter the intestines, intensively absorbing blood.
The substance looks like a colorless syrup, resembling honey or caramel paste in consistency. When dried, it turns into a white or light creamy powder, odorless, sweet in taste. It dissolves well in water of any temperature. It comes to the market mainly in the form of a powder, which, when rubbed by hand, resembles starch in consistency.
Depending on the method of production and on the raw materials, as well as its quality, different batches of maltodextrin may differ in 3 important points.
These are the following parameters:
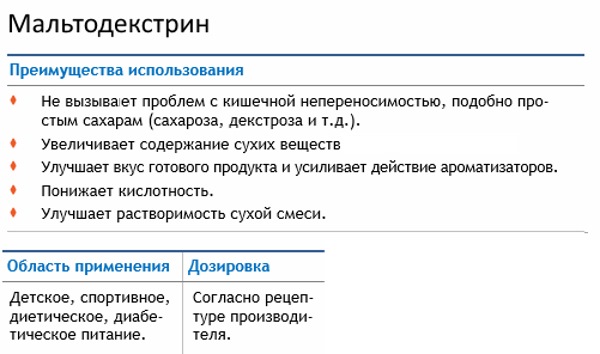
- Dextrose Equivalent (DE) - an indicator of the value of the restorative capacity of the product relative to glucose per 100 gr. dry matter (DE of glucose is 100). The deeper the hydrolysis of starch was performed during the preparation of the mixture, the higher its DE will be. For a powder product, this indicator can be in the range of 1-19 units, for syrups it can be much higher (up to 90 or more).
- Relative sweetness - an indicator of the sweetness of a substance in relation to sucrose. It is in the range of 0.1-0.5. Here there is an interdependence with the DE index, the higher this index, the higher the coefficient of relative sweetness.
- Physiological consistency (particle size and bulk density of the product). The finer the particles of the substance, the faster and easier they will mix with other components of the product without stratification. Bulk density saves space during storage and transportation of the product.
The most important functional properties of maltodextrin:
- participation in the creation of the structure of the product (can affect the density and viscosity, act as an emulsifier);
- an increase in the overall intensity of taste sensations;
- increased sensation of sweetness;
- inhibits sugar crystallization;
- serves as a fat substitute;
- increases the volume of the product;
- allows you to get a quick influx of energy.

 Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable haircut for short hair. Photo, front and back views.
Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable haircut for short hair. Photo, front and back views.Where is the substance contained
Maltodextrin is often found in common foods. It is included in many instant products and is used as a fat substitute.
List of foods in which this carbohydrate can be found:
- carbonated drinks;
- instant porridge;
- concentrated soups;
- sauces and salad dressings;
- semi-finished meat products;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- ice cream;
- sweets and marmalade;
- canned vegetables and fruits;
- bakery products;
- cereals;
- chips;
- frozen yoghurts;
- energetic drinks;
- nutritional bars;
- sports nutrition;
- powdered milk and baby food.
Food manufacturers prefer to use this carbohydrate for the following reasons:
- Serves as a preservative and increases the shelf life of the product.
- Mixes easily with other food ingredients.
- Contributes to obtaining the required thickness of the product with a uniform consistency.
- Increases product weight.
- It is a relatively inexpensive carbohydrate.
Properties of the substance. How does it affect the body
Maltodextrin is a very useful substance, which is characterized by such a number of positive qualities:
- is of natural origin;
- helps to reduce blood cholesterol;
- due to the high glucose content, energizes;
- has a higher digestibility than starches.
The use of the substance in the composition of food does not pose a threat to a healthy person, but is contraindicated for people suffering from diabetes mellitus and high obesity.
Although this complex carbohydrate is not classified as sugar, which allows manufacturers to label it "sugar free," it nonetheless has the same effects on the body as regular sugar, dramatically increasing blood glucose levels and promoting body fat storage.
For those with an allergic reaction to gluten, it is recommended to avoid the use of maltodextrin obtained from wheat starch.
What is it used for
Maltodextrin - This complex carbohydrate is not a food additive (Category E), which allows it to be classified as food.
In product formulations where it is present, it can also be found under other names, such as:
- syrup;
- glucose;
- grape or starch sugar;
- dextrose;
- dextrinmaltose.
Maltodextrin is used in several areas:
- Cooking... Has a wide range of applications, described below.
- Pharmacology... It is used as a prebiotic, as an inert excipient, to sweeten some drugs.
- Cosmetics. It is used to increase viscosity and increase shelf life in the production of shampoos, gels, and creams.
- Sports nutrition. Maltodextrin is a powerful source of carbohydrates.
- Another option for using maltodextrin is spraying it with a solution of fruits and berries, which protects them from pests, maintains freshness, and provides a presentation during storage and transportation.
Potential harm and side effects
The negative properties of the product include:
- the presence of a high glycemic index;
- negative impact on the intestinal microflora, increasing its vulnerability to infections;
- contributes to the gain of excess weight;
- lack of nutritional value;
- production of a product from raw materials containing GMOs is not excluded.
There are 4 side effects commonly seen with regular use of maltodextrin as a dietary supplement:
- Having a high glycemic index, carbohydrates can cause a sharp rise in blood sugar. It is easily absorbed and quickly enters the bloodstream. Dangerous for individuals with a predisposition to diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. The so-called reverse hypoglycemia is possible, which is expressed in a sharp decrease in blood sugar.
- May interfere with gut bacteria, negatively affecting the growth of beneficial probiotics, which can be expressed in flatulence and bloating due to increased bacterial activity. Promotes the survival of Salmonella, which in turn can lead to a number of chronic inflammatory diseases and exacerbate autoimmune disorders in the body.
- Allergic reactions are possible. So the conducted studies have confirmed that the use of maltodextrin can provoke a number of gastrointestinal problems, such as gas formation, seething, diarrhea. Allergic skin irritation has been reported. The manufacturers of the substance assure that maltodextrin cannot contain gluten and corn gluten, because during the processing of grain, starch and proteins are completely separated, therefore, in the production of maltodextrin, starch is used, devoid of protein impurities. However, experts are sure that we can only talk about a decrease in the gluten content in a manufactured product, but not about its complete absence.
- Weight gain. This factor is due to the fact that maltodextrin has the same effect on the body as ordinary sugar, having a high glycemic index, with an almost complete absence of nutrients in its composition, a complex carbohydrate contributes to the deposition of fatty deposits.

 Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable haircut for medium hair. Photo, front and back views.
Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable haircut for medium hair. Photo, front and back views.Maltodextrin application
In cooking
It has a wide range of applications, it is used as:
- emulsifier and thickener that improves the consistency of products;
- baking powder in the production of flour products (powder mixtures, dough);
- an element that improves the solubility of instant products;
- an ingredient that slows down the color changes of products during the oxidation process;
- sweetener for sauces and confectionery;
- shaping ingredient in jelly products;
- a stimulator of beneficial microflora in the intestines, an enhancer of digestibility.
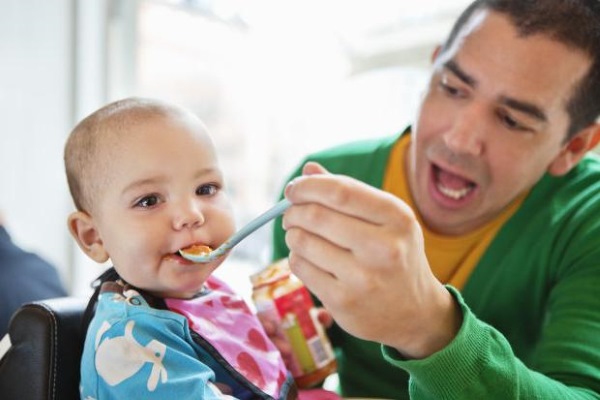
As part of baby food
Maltodextrin - what is it in baby food. In moderate concentration, it is included in cereals and mashed potatoes for babies, since it has a number of positive qualities directly for children of this age.
These positive properties are as follows:
- high digestibility, including the acceleration of protein absorption;
- the ability to replace sugar;
- has resistance to digestion by gastric juice, improves gastrointestinal motility;
- good source of energy;
With excessive use, it can negatively affect the intestinal microflora, but in baby food its amount is balanced. Baby food manufacturers have their own reasons to include maltodextrin in their products to the market.
They are guided by the following considerations:
- carbohydrate increases the satiety of the products in which it is used, replacing sugar and starch in them;
- used as a thickener;
- dissolves easily without forming lumps;
- increases the shelf life of the product;
- mixes well with other ingredients;
- it is easy to manufacture;
- the carbohydrate is cheap enough.
Maltodextrin does not represent pronounced harm to the health of the child.In the presence of this sweet-tasting carbohydrate in the product, the manufacturer has a legal opportunity to write on the packaging that the porridge or infant formula does not contain sugar.
In reality, when eating this product, the concentration of glucose in the blood is the same as when eating regular sugar.
This fact testifies to the contraindication of the use of products with this additive by children diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
A number of manufacturers claim that the carbohydrate they offer even lowers blood sugar levels, since in their production it is processed with acids and enzymes, and is exposed to heat. But so far there is no official confirmation of this information.
With frequent use of maltodextrin in baby food, the following consequences may occur:
- digestive problems, deterioration of intestinal microflora, flatulence, colic;
- decrease in resistance to infectious diseases;
- weight gain exceeding the age norm;
- hypovitaminosis (depletion of own reserves of vitamins and minerals);
- allergic reactions in case of gluten intolerance (celiac disease).
Children who are allergic to wheat and corn should be protected from foods containing maltodextrin, derived from the starches of these foods.
When purchasing baby food, you should pay attention to the country of origin. Typically, food made in Europe contains maltodextrin derived from wheat. Products from the USA and Canada contain maltodextrin made from cornstarch.
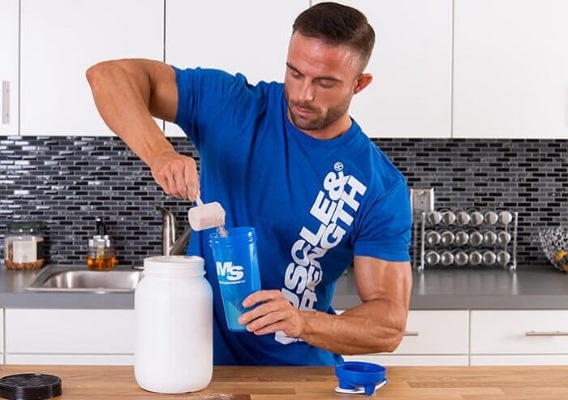
As part of sports nutrition
Maltodextrin - what is it in sports nutrition. This is not doping, it is officially approved for use. Since maltodextrin breaks down faster than normal glucose and is evenly distributed throughout the body, manufacturers and consumers of sports nutrition are showing increased interest in it.
It is produced as an independent preparation, which is a source of carbohydrates, and is also used as an excipient in complex mixtures and products.
A complex carbohydrate is used in the composition of sports nutrition (included in gainers - special sports nutritional supplements) before and after training in order to gain muscle mass, maintain and restore strength.
The drug is especially effective in sports where active muscular work is required under conditions of increased aerobic load.
Therefore, the carbohydrate is of particular interest to the following athletes:
- cyclists;
- rowers;
- swimmers;
- sprinters;
- boxers and wrestlers;
- representatives of game sports (hockey, basketball, football, etc.);
- tennis players;
- powerlifters, etc.
Athletes need to consume maltodextrin on training and competition days, otherwise an overdose of carbohydrates in the body may occur. When aerobic activity is high, it is preferable to consume it before and during exercise, as it is able to maintain normal blood sugar levels for a long time.
In sports nutrition, it is practiced to take maltodextrin along with whey protein, since it facilitates the penetration of protein amino acids into muscle tissue cells.
Slimming
It is recommended to avoid excessive consumption of foods rich in maltodextrin for people who are overweight and lead a sedentary lifestyle. The same recommendations apply to pregnant and lactating women.
Maltodextrin - what is it for people who want to lose weight. There is a weight loss technique using maltodextrin. The bottom line is this: with frequent and fractional meals, a small portion of the dietary product containing this carbohydrate is added to each meal.
This is done in order to constantly maintain a certain level of glucose in the blood without sharp fluctuations, which prevents the deposition of fat reserves.
In bodybuilding
Maltodextrin is very popular with bodybuilders because it helps maintain high blood glucose levels during exercise, which significantly increases the effectiveness of training. Another benefit is that it promotes rapid muscle building.
If there are no contraindications (predisposition to diabetes, allergic reactions), the use of maltodextrin in sports nutrition is considered justified and safe.
Product manufacturers and distributors often recommend it as the optimal source of carbohydrates, which is not entirely true.
The best effect is achieved by consuming carbohydrates immediately after training, which prevents athletes from losing some muscle fibers. One serving is 2-3 tablespoons of powder, which is 60-90 gr. You can make your own gainer by mixing 1 part protein with 3 parts maltodextrin.
In pharmacology
In pharmacology, maltodextrin is actively used in the production of drugs as an inert excipient; it simplifies the addition of ingredients with minimal dosages. Supplement manufacturers appreciate the ability of maltodextrin to stimulate the growth of intestinal microflora.
In cosmetology
Maltodextrin, what is it in cosmetology. The substance, as a structure-forming and auxiliary, is used in the manufacture of a number of cosmetics, such as balms, blush, dusting, and powder. An important component of the ingredient is in creams designed to cleanse pores and nourishing masks.
It is also present in some brands of toothpastes. In cosmetology, preference for use is given to maltodextrin, which has a low DE, since with such indicators, its ability to structure and regulate the viscosity of aqueous solutions is most realized.
In cosmetology, the following characteristics of maltodextrin are significant:
- acts as a viscosity regulator and an auxiliary thickening agent;
- exhibits anti-crystallization ability, which helps to increase the freezing point of the final product;
- endowed with a fixing function and the ability to enhance the aroma of the final product;
- acts as a hydrocolloid, showing moisturizing properties;
- allows to facilitate and improve the processes of dissolution of protein hydrolyzate and protein.
Particular attention is drawn to the use of maltodextrin in the production of anti-aging creams due to its ability to improve skin nutrition and reduce expression lines.

 Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable bangs of the new season for medium, short, long hair. A photo.
Don't miss the most popular column article: Fashionable bangs of the new season for medium, short, long hair. A photo.Top 5 best maltodextrin substitutes
If you have problems with sugar and obesity, it makes sense to exclude from consumption foods containing complex multicomponent carbohydrates, such as maltodextrin, and try to replace them with more natural and healthy counterparts.
The following products can act as such:
- Stevia... This natural sweetener is made from the leaves of the plant of the same name. There are three product varieties on the market: green leaf, extract, modified stevia. The most natural product, the least subject to processing, is the green leaf.
- Pectin. A natural product obtained primarily from fruits (apples, pears, plums, citrus fruits), as well as vegetables and seeds. Used as a thickener, stabilizer, gelling agent. It has a high fiber content, which has a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system. Binds and removes cholesterol, fats and toxins from the body.
- Guar gum. It is obtained by extracting the seeds of the guar (pea tree) legume, which grows in India. Used as a thickener.It has a feature - to slow down the absorption of glucose, which is a positive moment for people with high cholesterol levels and a tendency to diabetes.
- Honey. Fresh honey, which has not undergone filtration and pasteurization, is especially valuable. It is highly digestible and contains a high percentage of natural sugars. It has a positive effect on the immune system by increasing the level of antioxidants in the body.
- Dates. They are rich in trace elements (potassium, copper, magnesium, iron, manganese) and vitamin B6. Promote more complete absorption of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
Specialists in dietetics and medicine note that it is impossible to unequivocally relate to such a substance as maltodextrin, it would be a mistake. It is obvious that it can have both positive and negative effects on the body, depending on the method of consumption, additional food ingredients, human health and many other factors.
Article design: Svetlana Ovsyanikova
Video on the topic: Maltodextrin - application in sports nutrition
The use of maltodextrim in sports nutrition:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g9-yHSA1Tvo
Sports nutrition - gainers: what it is, the benefits and harms:











A good drug according to reviews, but my body reacts badly to it - immediately flatulence, bubbling in the stomach and other delights. Experts say - an individual reaction of the body.